Model #
The evaluation of breeding value for production traits and somatic cell count (SCC) is based on the analysis of daily milk yield, fat, protein, and lactose content as well as the number of somatic cells (SCC). Test milkings conducted in the same herd on the same day are classified into one subclass called herd test day.
Breeding values are estimated using a single-trait, multi-lactation (limited to the first three lactations) method called BLUP – animal model with random regression.
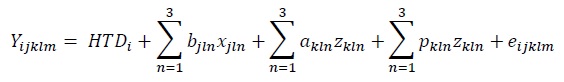
where:
- Yijklm m-th daily yield of milk, fat, protein, lactose or SCS for the k-th cow in the l-th lactation, in the i-th subclass of milking day in the herd, in the j-th subclass of age at calving-season of calving-breed-period of time,
- HTDi random effect of milking day in the herd,
- bjln constant regression coefficients in subclasses of age at calving-season of calving-breed-period of time.
- akln random regression coefficients for additive genetic effect.
- pkln random regression coefficients for permanent environmental effect.
- xjln and zkln covariates calculated based on lactation day.
- eijklm random error effect.
A total of 12 age classes of calving were created, including 5 classes within the first lactation, 4 classes within the second lactation, and 3 classes within the third lactation, 2 calving seasons (April-September and October-March), and time periods consisting of three consecutive calving years (starting from 1995). The lactation curves in age class-subclass-calving season-variety-time period are modeled using the Wilmink function, while the remaining lactation curves are modeled using second-degree Legendre polynomials. A homogeneous distribution of error variance is assumed for each day of lactation.
Breeding values for the percentage content of fat, protein, and lactose are calculated based on estimated breeding values for milk yield, fat, protein, and lactose yield, as well as the average milk yield and percentage content of fat, protein, and lactose in the second lactation of cows born in the year adopted as the genetic base.
Scope and types of observations #
The evaluation takes into account data for cows calved after January 1, 1995. The evaluation method distinguishes whether the daily milk yield is the sum of the morning and evening yield (A4 and A8 evaluation methods) or is calculated based on only the morning or only the evening milking (AT4 evaluation method). Observations from the AT4 system are given less weight, i.e. for the A4 and A8 methods, a weight of 100% is assumed, and for the AT4 method, a weight of 80% is assumed.
The number of somatic cells SCC in the test milkings is subjected to logarithmic transformation according to the formula below, obtaining the somatic cell content SCS.
SCS = log 2 (SCC ⁄ 100000) + 3
Genetic groups #
Genetic groups are created for unknown parents of evaluated animals. The term “unknown parents” in this case means a lack of information about the parents. All other evaluated animals are assigned to genetic groups indirectly, through pedigree relationships. Three separate genetic groups were created for bull-sires and nine genetic groups for cow-dams. Within each sex, a division was also adopted based on age and the share of HF genes. The birth year of animals that do not have this information is estimated based on the known birth dates of their relatives.
Corrections for heteroscedasticity in herd-year variance #
In order to adjust for differences in variability of daily performance and SCS within herds, corrections for heteroscedasticity were applied.
Genetic parameters #
The heritability values presented in Table 1 were used to estimate the breeding values of the animals.
| Lactational milk yiels | | | | |
| milk | fat | protein | lactosis | SCS |
| 0,33 | 0,29 | 0,29 | 0,30 | 0,32 |
The method of expressing breeding value #
By using the method based on test milking, animal breeding values are obtained for each day of lactation. The sum of these values from day 5 to 305 after calving gives the so-called lactation breeding value. The breeding value of an animal is calculated as the arithmetic average of the breeding values for the first three lactations. Before averaging, the variability of scores in the second and third lactations is standardized to the level of variability in the first lactation. When calculating the variability of scores, breeding values for bulls based on a minimum of 10 daughters are taken into account.
The BLUP multi-lactation model for animals, utilizing the genetic connections between lactations, enables the estimation of breeding values for each lactation, even if data is missing.
Genetic base #
The average breeding value of cows born in 2015 is adopted as the genetic base. The breeding values of all cows and bulls are expressed as deviations from the base.
Production index (in kg) #
The production index takes into account breeding values for fat and protein yield:
Index [kg] = breeding value for fat yield [kg] + 2 * breeding value for protein yield [kg]
Production sub-index #
The production sub-index (PI_PROD) = breeding value for fat + 2 * breeding value for protein.
Breeding values for performance traits prior to the creation of the production sub-index (PI_PROD), which is one of the components of the overall index, were standardized to a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 10, using the average breeding value of bulls born between 2009 and 2011 and having at least 20 daughters in 10 herds as the base value.